
Fume hoods are designed to provide personnel protection from toxic or volatile chemicals by continuously delivering airflow away from the user to the work area. Air is then filtered and/or treated by the building’s exhaust system before exiting the facility (ducted) or by filters contained in the fume hoods, which clean the contaminated air and recirculate it directly back into the laboratory (ductless).
The Benefits of a Ductless Laboratory – Clean Air is Expensive
Ductless fume hoods provide the same filtration capabilities as ducted hoods, but are easier to install, have lower initial installation costs and can be highly efficient. They are equipped with numerous technological advances to enhance safety and function. Low airflow alarms ensure the proper containment of fumes inside the hood, filter saturation alarms help maintain near to zero chemical emissions in recirculated air and backup safety filters protect against filter malfunction. In fact, ductless fume hoods require very little energy to operate compared to ducted hoods.
Fume Hood Design and Operation
The primary purpose of the fume hood is to contain gases, vapors and fumes and then exhaust them out of the area. The fume hood begins this process by pulling room air into and through the fume. The air enters the hood through the sash. Depending on its design, the sash may move vertically or horizontally, or a combination of the two. The sash also acts as a barrier between the worker and the inside of the fume hood and provides limited protection.
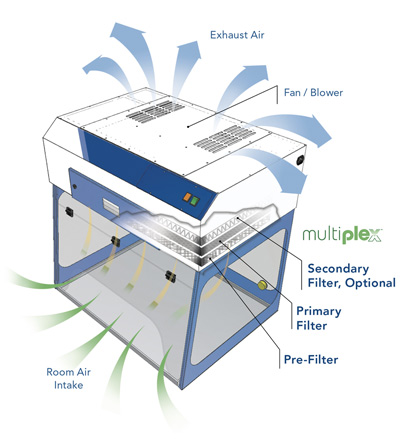
As the air flow works its way through the middle of the fume hood, it pushes the harmful gases, vapors and fumes toward the exhaust area. This area is managed by slots and baffles which act as exit doors for the fume hood before reaching either the connected ductwork (ducted fume hood) or the fume hood filters (ductless fume hood). In many fume hoods, the slots and baffles are adjusted to allow for even air flow.
If the baffles are closed (or blocked) the exhaust path will also be blocked. But when used properly, baffles eliminate dead spots or reverse air flows which would result in a loss of containment. After air exits the fume hood it is transported through ductwork to where it is released into the atmosphere; or on ductless fume hoods, the air is filtered and recirculated back into the room.
Air Science manufactures a complete series of high efficiency ductless fume hoods, ductless workstations and total exhaust fume hoods designed to protect the user, the process and the environment from hazardous vapors, fumes and particulates.
Resources

Evolution of a Ductless Fume Hood

Which is Better – Horizontal or Vertical Laminar Flow Clean Benches?
