Get the Best Results for Your Application
What is a laminar flow hood?
Laminar flow hoods go by a few names, including laminar flow cabinets, laminar flow workstations, or clean benches. Regardless of their name, a laminar flow hood is a workstation designed to provide an aseptic workspace for non-hazardous applications that must avoid particulate contamination. Applications requiring operator and environmental protection from hazardous or potentially hazardous materials on the work surface should use biological safety cabinets (BSCs).
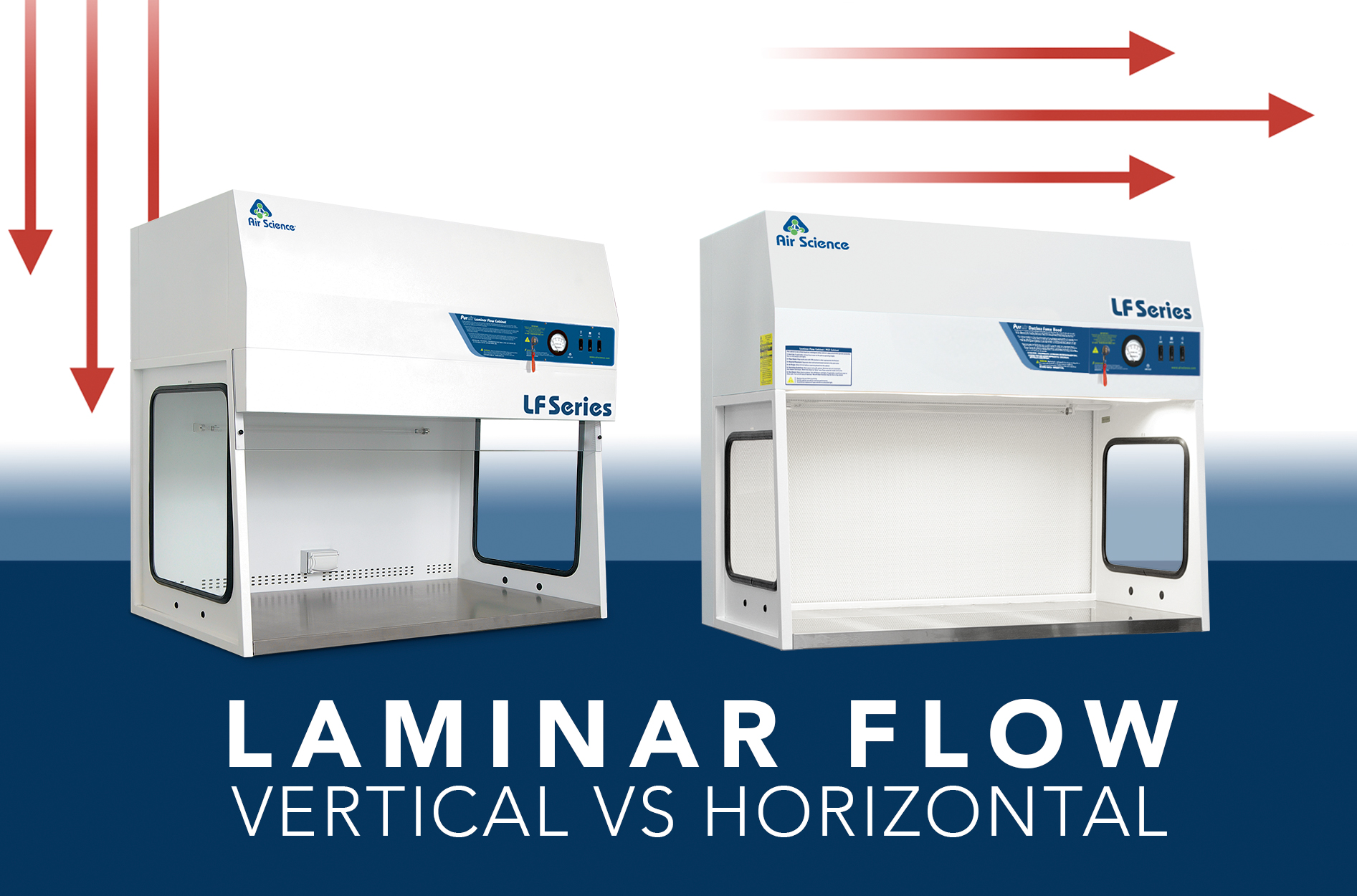
Laminar flow hoods generate a consistent, unidirectional flow of HEPA or ULPA-filtered air that passes either parallel to the work surface (horizontally) or from the top of the unit down (vertically). High quality laminar flow hoods minimize turbulence from items inside the enclosure.
When deciding between a horizontal or vertical laminar flow hood, it is important to consider the type of application for which you need the hood.
What type of laminar flow hood do I need?
Choose a horizontal laminar flow hood if your application has the following needs:
- Airflow turbulence on the work surface must be minimal.
- Equipment used on the work surface mostly consists of small items and utensils.
- Greater contamination control is needed.
Choose a vertical laminar flow hood if your application has the following needs:
- Equipment used on the work surface is larger.
- Fine powders will be on the work surface.
- A taller or larger workspace is needed.
What are the differences between horizontal and vertical laminar flow hoods?
In a horizontal laminar flow hood, the HEPA/ULPA filter is located on the back wall. Positive pressure streams of the filtered air move through the work zone, parallel to the work surface, before exhausting out the front of the cabinet.
The HEPA/ULPA filter is located above the work surface in vertical laminar flow cabinets. The positive pressure filtered air then moves down vertically, striking the work surface and exhausting out the cabinet front. On some laminar flow hoods, perforations on the back wall also allow air to exhaust, reducing work surface turbulence.
What are the advantages of horizontal laminar flow hoods?
Horizontal laminar flow hoods have the following advantages:
- Though turbulent effects are still minimal in a vertical laminar flow hood, horizontal laminar air does provide even less turbulence since airflow is parallel to the work surface.
- It is easier to position and stagger sterile equipment and materials on the work surface closer to the filter face (upstream from other potential contaminants).
- Since they’re downstream of the sample, contamination from hands in the work zone is reduced.
What are the disadvantages of horizontal laminar flow hoods?
Horizontal laminar flow hoods have the following disadvantages:
- Filter change or service usually requires repositioning a horizontal laminar flow hood to allow for rear access.
- Large samples can obstruct laminar airflow in a horizontal laminar flow hood and may contaminate downstream samples.
- Fumes or powders can be blown into the operator’s face if a horizontal laminar flow hood is used without a sash.
What are the advantages of vertical laminar flow hoods?
Vertical laminar flow hoods have the following advantages:
- Airflow perpendicular to the work surface and a sash reduce air, and powders on the work surface, from blowing onto the workstation operator.
- The location of the filter on top of the unit makes filter changes easier and provides more working height to accommodate tall or large equipment.
- The reduced turbulent effect from air striking large objects or processing equipment means less cross-contamination of items on the work surface.
What are the disadvantages of vertical laminar flow hoods?
Vertical laminar flow hoods have the following disadvantages:
- Taller workstations can increase overhead clearance requirements and make it necessary to use a ladder or stepstool during filter changes.
- Placing hands or other items inside the workspace can obstruct airflow.
- Air turbulence is slightly increased when compared to horizontal laminar flow hoods as the air flow is perpendicular to the work surface.
How can I reduce contamination in my laminar flow hood?
Proper cleaning methods and regular maintenance will ensure your laminar flow cabinet provides safe and accurate results. Follow these 10 tips to keep your laminar flow hood clean.
Air Science Laminar Flow Hoods
Air Science offers vertical and horizontal laminar flow hoods with easy-to-change filters and customizable options. Our Laminar Flow Hood product line relies on Air Science Multiplex™ HEPA/ULPA Filtration Technology to help ensure a clean work environment over a wide range of applications.
Looking to purchase your next laminar flow hood?
